This browser-based utility generates triples of integers and prints them as three-dimensional xyz coordinates in the output. You can specify three individual ranges for each coordinate and also indicate how many triples to output. The output format of triples can be customized as well by adjusting the brackets around triples and changing the separators between each coordinate. Created by math nerds from team Browserling.
This browser-based utility generates triples of integers and prints them as three-dimensional xyz coordinates in the output. You can specify three individual ranges for each coordinate and also indicate how many triples to output. The output format of triples can be customized as well by adjusting the brackets around triples and changing the separators between each coordinate. Created by math nerds from team Browserling.
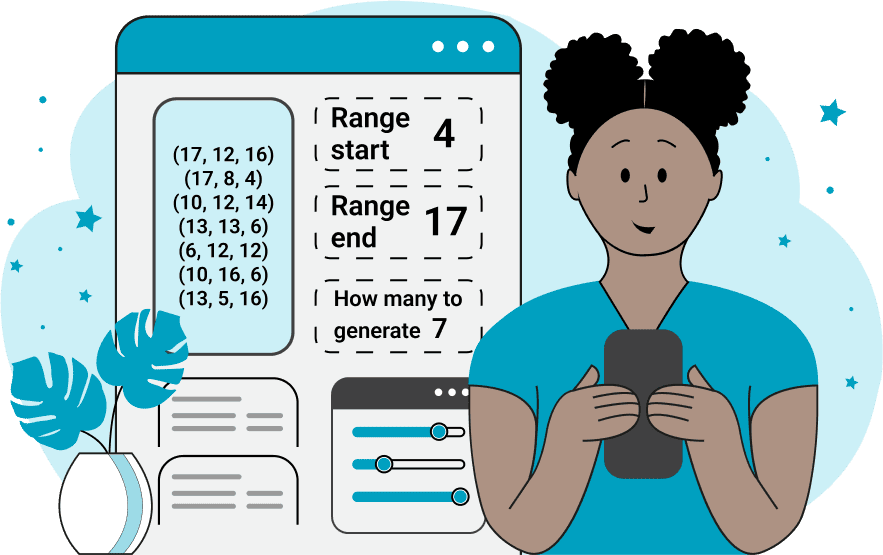
With this online application, you can generate random triplets of integers. The combination of three integers represents a point in the three-dimensional Cartesian space and it's written in the form (x, y, z), where x is the abscissa of the point, y is the ordinate of the point, and z is the applicate of the point. As all coordinates are independent, you can control the range of each one of them independently. In the first options block, you are given six cells for range values. Every two cells correspond to the start and end values of a coordinate. The first coordinate is generated by randomly picking an integer from the range [start_x, end_x], the second coordinate is selected from range [start_y, end_y], and the third from the range [start_z, end_z]. Both start and end values are included in the range. In the second block of options, you can specify how many triplets of integers to generate and also configure the delimiter character between the points. The third block of options allows you to change the format of coordinates. By default points, are opened and closed through the "(" and ")" symbols but you can use any character to open and close the point. You can also change integer delimiters. By default, the comma symbols are used between "x, y" and "y, z" values but you can put any symbol between these values. 3D-abulous!
With this online application, you can generate random triplets of integers. The combination of three integers represents a point in the three-dimensional Cartesian space and it's written in the form (x, y, z), where x is the abscissa of the point, y is the ordinate of the point, and z is the applicate of the point. As all coordinates are independent, you can control the range of each one of them independently. In the first options block, you are given six cells for range values. Every two cells correspond to the start and end values of a coordinate. The first coordinate is generated by randomly picking an integer from the range [start_x, end_x], the second coordinate is selected from range [start_y, end_y], and the third from the range [start_z, end_z]. Both start and end values are included in the range. In the second block of options, you can specify how many triplets of integers to generate and also configure the delimiter character between the points. The third block of options allows you to change the format of coordinates. By default points, are opened and closed through the "(" and ")" symbols but you can use any character to open and close the point. You can also change integer delimiters. By default, the comma symbols are used between "x, y" and "y, z" values but you can put any symbol between these values. 3D-abulous!
In this example, we generate eight triplets of natural numbers. Each coordinate uses a different range of numbers. The abscissa x contains all natural numbers less than 10. The ordinate y is generated from all positive two-digit integers from 10 to 99. The applicate z uses all three-digit values from 100 to 999. We also add round parentheses around triplets and separate coordinates by commas.
This example demonstrates an unusual application of integer triplets. It generates random digital clock times. Clock times can be broken into three variables: hours, minutes, and seconds. Therefore, for the first coordinate (hours), we set the range of integers to be from 0 to 23, for the second coordinate (minutes), we set the range to be from 0 to 59, and for the third (seconds), the range is from 0 to 59. We separate the integers by the colon characters and remove the parentheses on the sides. We generate fifteen random clock times and print them one after another, separating them by a comma.
In this example, we modify every detail of the points and create a weird set of triples. We wrap the coordinates in square brackets "[]" and separate them by two glyphs "><". We use a negative range from -200 to -100 for the first parameter, a single digit for the second parameter, and the integer 0 for the third parameter (range 0 to 0 always returns 0). We also use different separators for the parameters. The semicolon is used between x and y and the dot is used between y and z coordinates.
You can pass options to this tool using their codes as query arguments and it will automatically compute output. To get the code of an option, just hover over its icon. Here's how to type it in your browser's address bar. Click to try!
Create a drawing that visualizes von Neumann hierarchy of sets.
Create a sudoku puzzle.
Create a list of neat-looking integers (called magic integers).
Generate a list of tuples of integers with n elements.
Quickly convert integers to base one.
Quickly convert base one to integers.
Quickly convert integers to base two.
Quickly convert base two to integers.
Quickly convert integers to base eight.
Quickly convert base eight to integers.
Quickly convert integers to base sixteen.
Quickly convert base sixteen to integers.
Quickly encode integers to base-64.
Quickly decode base-64 to integers.
Quickly convert integers to a custom base.
Quickly encode integers to HTML encoding.
Quickly decode HTML entities to integers.
Quickly encode integers to URL (percent) encoding.
Quickly decode URL-encoded integers.
Quickly convert a signed integer to an unsigned integer.
Quickly convert an unsigned integer to a signed integer.
Generate a list of random integers.
Check if the given integers are palindromes.
Create a matrix whose entries are all integers.
Create a vector with integer coefficients.
Quickly calculate the average value of integers.
Quickly calculate the average value of integer digits.
Quickly randomly select a digit from an integer.
Find which of the given integers is the biggest or smallest.
Limit integer values to a range.
Limit integer digit values to a range.
Create multiple copies of the input integers.
Create multiple copies of digits of input integers.
Rotate the digits of an integer to the left or right.
Move the digits of an integer to the left or right.
Quickly find the difference of a bunch of integers.
Quickly apply the bitwise AND operation to integers.
Quickly apply the bitwise OR operation to integers.
Quickly apply the bitwise XOR operation to integers.
Quickly apply the bitwise NOT operation to integers.
Quickly apply the bitwise NAND operation to integers.
Quickly apply the bitwise NOR operation to integers.
Quickly apply the bitwise NXOR operation to integers.
Quickly divide two or more integers.
Quickly divide the digits of an integer.
Add -st, -nd, -rd, -th suffixes to integers to make them ordinals.
Remove -st, -nd, -rd, -th suffixes from ordinals to make them ints.
Find integers that match a filter (greater, less, equal).
Add padding to integers on the left side.
Add padding to integers on the right side.
Position all integers so that they align on the right.
Position all integers so that they align in the middle.
Turn all integers into positive integers.
Turn all integers into negative integers.
Rewrite an integer in fractional form.
Extract the numerator and denominator from a fraction.
Search for all occurrences of an integer and replace it.
Create a regex that matches the given integers.
Create integers that match the given regular expression.
Create relatively tiny integers.
Create relatively huge integers.
Create a sequence of oscillating integers, such as 123212321.
Create multiple integer sequences at once.
Slightly change an integer so it has an error.
Slightly change integer digits so there are errors.
Apply fuzzing to integers and add perturbations.
Apply fuzzing to integer digits and add digit perturbations.
Add highlighting to certain integers.
Add highlighting to certain integer digits.
Add color to integers based on a condition.
Add color to individual digits in the given integers.
Quickly assign colors to integers and draw them as pixels.
Quickly assign integer values to pixel colors and print them.
Make the digits of an integer go in a spiral shape.
Make the digits of an integer go in a circle.
Make the digits of an integer go in a diamond shape.
Fill a box with certain width and height with digits.
Use ASCII art to convert integers to 2-dimensional drawings.
Use ASCII art to convert integers to 3-dimensional drawings.
Decompose an integer into ones, tens, hundreds, etc.
Generate an ordered list of increasing integers.
Generate an ordered list of decreasing integers.
Quickly find various information about the given integers.
Find hidden patterns of numbers in integers.
Find the Shannon entropy of an integer.
Subscribe to our updates. We'll let you know when we release new tools, features, and organize online workshops.
Enter your email here
We're Browserling — a friendly and fun cross-browser testing company powered by alien technology. At Browserling our mission is to make people's lives easier, so we created this collection of integer tools. Our tools have the simplest user interface that doesn't require advanced computer skills and they are used by millions of people every month. Our integer tools are actually powered by our programming tools that we created over the last couple of years. Check them out!